The Ultimate Showdown: Paleo Diet vs Keto

Are you ready for the ultimate battle of the diets?
In one corner, we have the Paleo Diet – a lifestyle that takes us back to our hunter-gatherer roots. And in the other corner, we have the Keto Diet – a low-carb, high-fat regimen that aims to put your body into a state of ketosis.
Both diets have gained a massive following, promising weight loss, improved health, and increased energy levels. But which one reigns supreme?
Let’s unpack the differences, benefits, and drawbacks of the Paleo Diet versus Keto, and find out which approach might be the perfect match for you.
Overview of Paleo Diet and Keto

What is the Paleo Diet?
The Paleo Diet, also known as the Paleolithic Diet or the Caveman Diet, is based on the dietary patterns of our ancient ancestors. The main principle behind this diet is to consume foods that were available to humans during the Paleolithic era, before the advent of agriculture. The diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. Grains, legumes, dairy products, refined sugars, and processed foods are excluded from the Paleo Diet.
What is the Keto Diet?
The Keto Diet, short for ketogenic diet, is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that aims to induce a state of ketosis in the body. Ketosis occurs when the body’s primary source of fuel switches from carbohydrates to fat. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the body enters a metabolic state in which it produces ketones for energy. The primary focus of the Keto Diet is limiting carbohydrates, promoting moderate protein intake, and consuming high amounts of healthy fats.
Key Similarities and Differences
While both the Paleo Diet and the Keto Diet share the goal of promoting health and weight loss, there are significant differences between the two.
The main similarity is that both diets emphasize the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods and discourage the consumption of refined sugars and processed foods. They also promote a higher intake of healthy fats compared to the standard Western diet.
The major difference lies in their macronutrient composition. The Paleo Diet allows for a moderate intake of carbohydrates, primarily from fruits and vegetables. On the other hand, the Keto Diet strictly restricts carbohydrate intake to a level that induces ketosis. This means the Keto Diet is much lower in carbohydrates and higher in fats compared to the Paleo Diet.
Another difference is the source of fats. The Paleo Diet encourages the consumption of healthy fats from sources such as nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil. The Keto Diet, however, focuses on consuming high amounts of saturated fats, such as those found in animal products, coconut oil, and butter.
Nutritional Composition

Macronutrient Ratios
The macronutrient ratios of the Paleo Diet and the Keto Diet differ significantly.
The Paleo Diet typically consists of approximately 30% protein, 30% fat, and 40% carbohydrates. This macronutrient distribution is closer to the recommended dietary guidelines for a balanced and sustainable diet.
In contrast, the Keto Diet follows a strict macronutrient ratio, commonly known as the 75/20/5 rule. This means that approximately 75% of calories consumed come from fat, 20% from protein, and only 5% from carbohydrates.
Carbohydrate Intake
The carbohydrate intake on the Paleo Diet is moderate compared to the significantly restricted carbohydrate intake on the Keto Diet.
On the Paleo Diet, carbohydrates primarily come from fruits, vegetables, and some starchy tubers. This allows for a broader range of carbohydrate choices, which can provide essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants.
In contrast, the Keto Diet limits carbohydrate intake to approximately 20 to 50 grams per day, depending on individual needs. This extremely low carbohydrate intake forces the body into a state of ketosis, where it relies on fat for fuel instead of glucose.
Protein Sources
Both the Paleo Diet and the Keto Diet prioritize protein intake, but the sources and quantities may vary.
The Paleo Diet promotes the consumption of lean meats, fish, seafood, and eggs as primary sources of protein. This provides essential amino acids for muscle growth, repair, and overall health.
The Keto Diet also emphasizes protein intake, but it is important to moderate and choose sources that are not high in carbohydrates. This includes foods such as poultry, beef, pork, and fatty fish. It is important to note that excessive protein consumption on the Keto Diet can hinder ketosis, as protein can be converted into glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis.
Fat Consumption
Fat consumption is a key aspect of both diets, but the types of fats and quantities may differ.
The Paleo Diet encourages the consumption of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and coconut oil. These fats provide essential fatty acids, promote satiety, and have shown potential health benefits.
The Keto Diet requires a high intake of healthy fats, including saturated fats. This may include foods such as butter, coconut oil, animal fats, and high-fat dairy products. The emphasis on saturated fats in the Keto Diet is due to its role in supporting ketosis and providing a readily available source of energy.
Health Benefits
Weight Loss
Both the Paleo Diet and the Keto Diet have been associated with weight loss.
The Paleo Diet promotes weight loss through its emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods and the elimination of processed sugars and refined carbohydrates. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods and limiting calorie-dense options, many individuals experience appetite control and improved body composition.
The Keto Diet’s ability to induce ketosis and shift the body’s primary fuel source to fat can lead to significant weight loss. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, the body is forced to burn stored fat for energy, resulting in accelerated fat loss.
Improved Energy Levels
Many individuals report increased energy levels when following either the Paleo Diet or the Keto Diet.
On the Paleo Diet, the elimination of processed foods and refined sugars reduces energy crashes caused by blood sugar spikes and crashes. Instead, the focus on whole foods provides sustained energy throughout the day.
The Keto Diet promotes stable energy levels by utilizing fat as the body’s primary fuel source. By avoiding blood sugar fluctuations associated with high carbohydrate intake and relying on ketones for energy, individuals often experience sustained energy, improved mental clarity, and reduced energy crashes.
In conclusion, while both the Paleo and Keto diets focus on whole foods and restrict certain food groups, they differ in their macronutrient composition and underlying principles. The Paleo diet emphasizes consuming foods that our ancestors would have eaten, focusing on quality sources of protein and unprocessed foods. In contrast, the Keto diet is more about manipulating macronutrient ratios to achieve a metabolic state that promotes fat burning.
One key difference between the two diets is their stance on carbohydrates. The Paleo diet allows for a moderate intake of carbohydrates from fruits and vegetables, while the Keto diet severely restricts carbohydrate consumption to maintain ketosis. Additionally, the Paleo diet does not specifically dictate macronutrient ratios but rather encourages whole food choices.
In terms of potential benefits, both diets have been associated with weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and increased energy levels. However, individual responses to these diets can vary based on factors such as metabolic health, activity level, and personal preferences.
In conclusion, the Paleo diet focuses on mimicking ancestral eating patterns with an emphasis on whole foods, while the Keto diet aims to shift the body’s metabolism towards burning fat for fuel through strict carbohydrate restriction. Both diets have their unique approaches and potential benefits for different individuals seeking to improve their health and well-being.
Share:
Related Posts
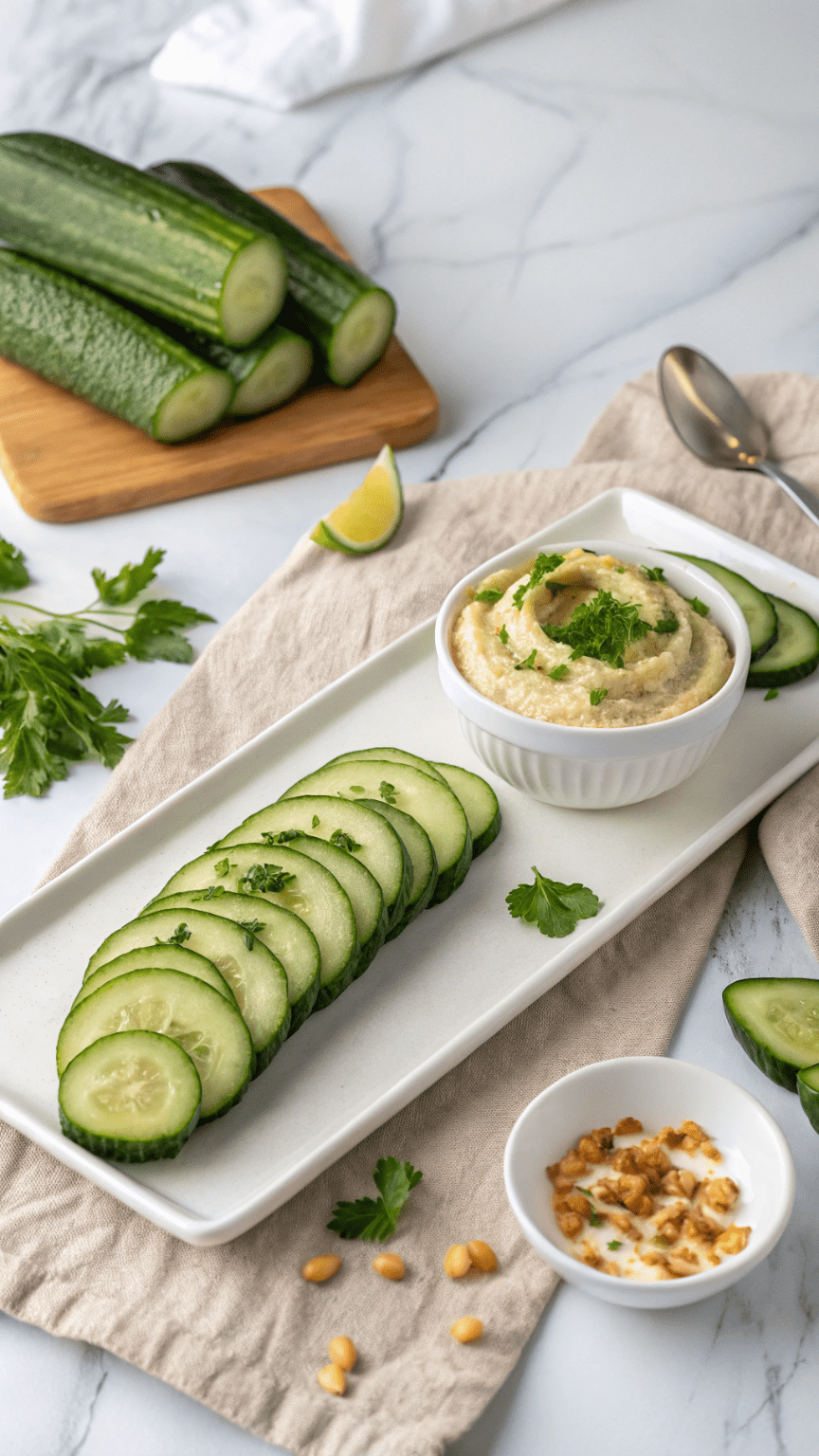

Quick & Super Easy Cucumber & Hummus
Stay energized with this fresh and healthy Cucumber & Hummus snack! Perfect for a quick bite, it’s low-calorie, nutrient-rich, and takes just 5 minutes to make.
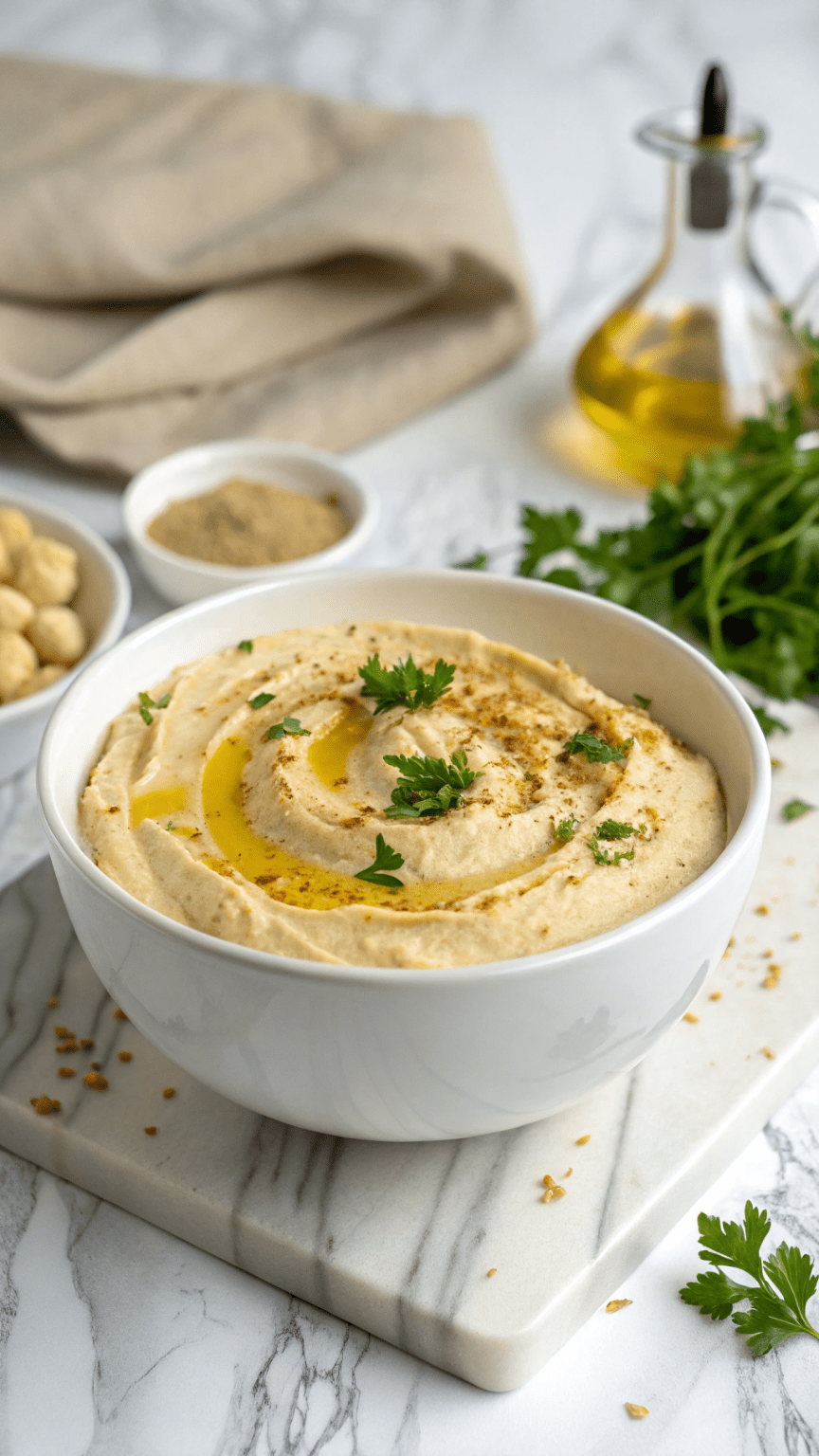

Easy Homemade Hummus
Creamy, smooth, and delicious—this easy homemade hummus recipe is packed with plant-based protein, healthy fats, and bold Mediterranean flavor. Perfect for dipping or spreading!
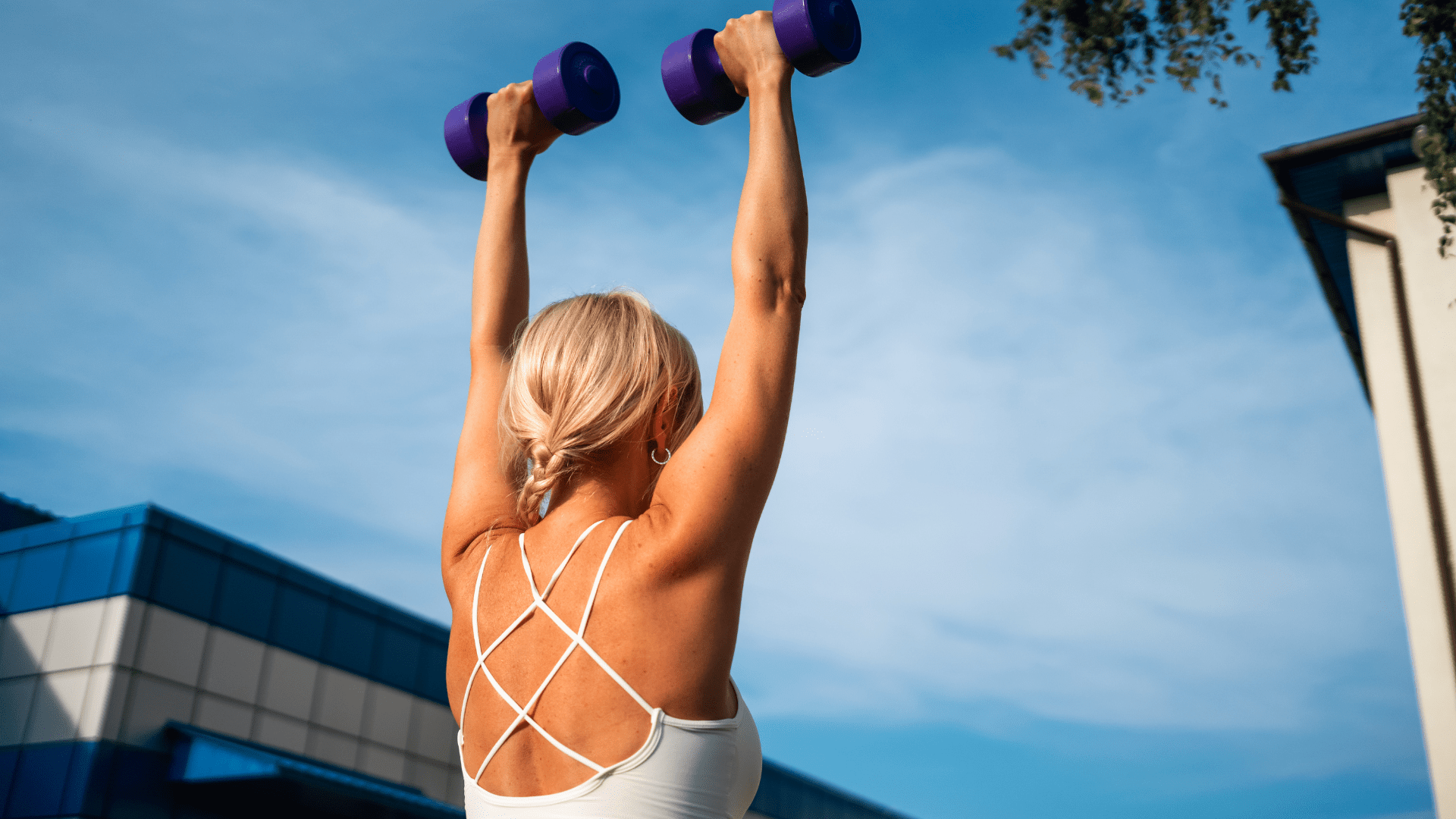

Upper Body Strength Training for Women
Discover how to start upper body strength training for women with this beginner-friendly guide. Learn easy exercises, tips, and routines to build strength and confidence.
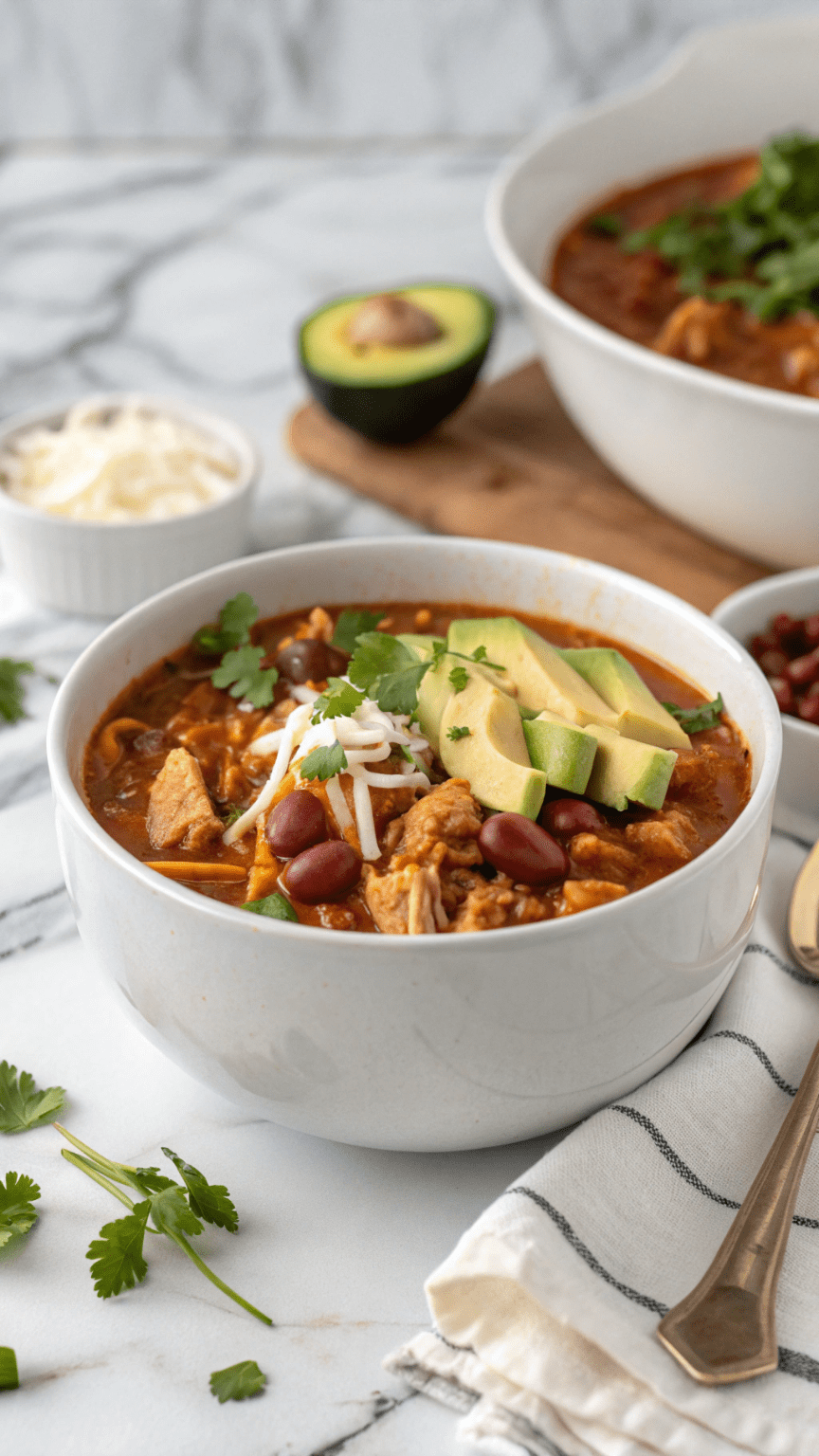

High-Protein Chicken Chili
This High-Protein Chicken Chili is hearty, flavorful, and packed with lean protein. Perfect for meal prep, weeknight dinners, or post-workout fuel.