The Complete Guide to an Anti-Candida Diet

Are you looking for a way to balance your gut health and eliminate Candida overgrowth? Look no further than “The Complete Guide to an Anti-Candida Diet.”
In this comprehensive guide, you will uncover the key principles and strategies behind an effective anti-Candida diet. From understanding the causes of Candida overgrowth to learning about the foods to include and avoid, this guide will equip you with all the knowledge you need to embark on a journey towards better gut health. Say goodbye to pesky Candida symptoms and hello to a healthier you
Understanding Candida Overgrowth
Candida overgrowth, also known as Candidiasis, occurs when there is an imbalance of the yeast Candida in the body. While Candida is naturally present in small amounts in the digestive system and on the skin, certain factors can lead to its overgrowth. When this happens, it can cause a range of health issues and symptoms, making it important to understand and address Candida overgrowth.
What is Candida?
Candida refers to a group of yeast species that can exist in different parts of the body, including the gut, mouth, and vagina. Candida albicans is the most common type and is usually harmless in small amounts. However, when conditions such as a weakened immune system, imbalanced gut flora, or a high sugar diet are present, Candida can multiply and overtake the beneficial bacteria.
Causes of Candida Overgrowth
Several factors can contribute to the development of Candida overgrowth. These include a diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates, excessive alcohol consumption, prolonged use of antibiotics, weakened immune system, hormonal imbalances, chronic stress, and certain medical conditions. It’s essential to identify the underlying causes to effectively address Candida overgrowth and prevent its recurrence.
Symptoms of Candida Overgrowth
Candida overgrowth can manifest in various ways, and the symptoms can differ from person to person. Some common symptoms include fatigue, brain fog, recurring yeast infections, digestive issues like bloating and gas, skin rashes, allergies, mood swings, and weakened immune function. If you suspect Candida overgrowth, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Principles of an Anti-Candida Diet
The foundation of an anti-Candida diet involves eliminating foods that promote Candida overgrowth and supporting the body with nutrient-rich options. Here are the key principles of an anti-Candida diet.
Elimination of Sugar and Yeast
Candida feeds on sugar, so eliminating all forms of refined sugar, including table sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, and artificial sweeteners, is crucial. Additionally, avoiding foods and beverages containing yeast, such as bread, pastries, and alcohol, can help to starve the Candida and prevent its growth.
Reducing Carbohydrate Intake
Candida also thrives on carbohydrates, particularly refined and processed ones. To combat overgrowth, it’s important to reduce your intake of starchy foods like white bread, pasta, and rice. Instead, focus on consuming complex carbohydrates from whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, which provide necessary fiber and nutrients without promoting Candida growth.
Including Anti-Fungal Foods
Incorporating anti-fungal foods into your diet can help combat Candida overgrowth. These include garlic, onions, coconut oil, ginger, oregano, and cinnamon, which have been shown to possess anti-fungal properties. These foods can help to inhibit the growth of Candida and support the body’s natural defenses.
Foods to Include in an Anti-Candida Diet
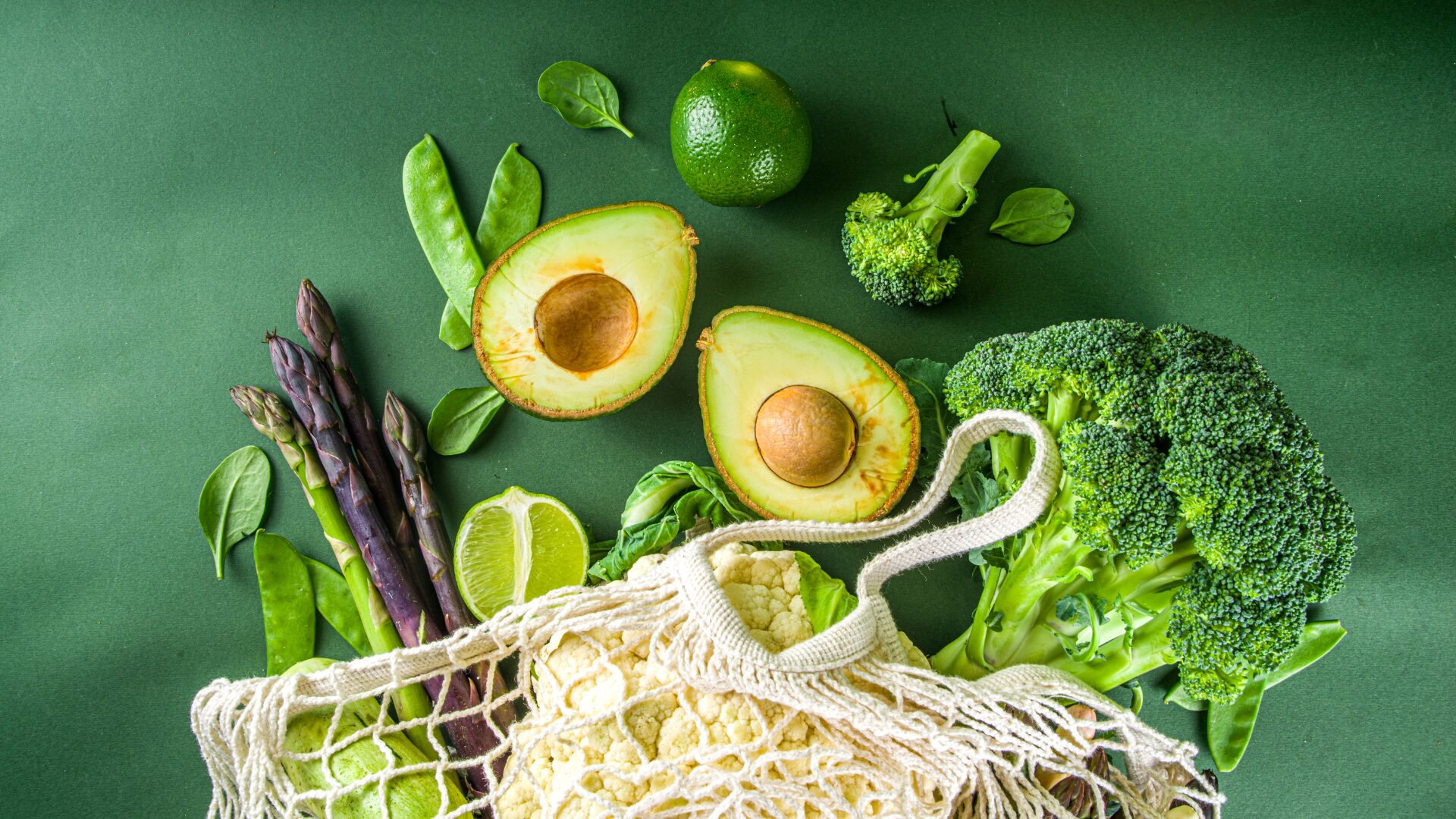

When following an anti-Candida diet, it’s important to focus on nutrient-dense foods that support overall health and balance in the body. Here are some categories of foods to include in your anti-Candida diet:
Non-Starchy Vegetables
Non-starchy vegetables are an essential component of an anti-Candida diet. These include leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, zucchini, and cucumbers. These vegetables are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an excellent choice to nourish the body and support optimal digestion.
Low-Sugar Fruits
While some fruits contain natural sugars, there are still options that can be enjoyed in moderation on an anti-Candida diet. Examples include berries like blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries, which are lower in sugar compared to tropical fruits like mangoes and pineapples. Choosing lower-sugar fruits will limit the food source available for Candida.
Protein Sources
Protein is essential for repairing and rebuilding tissues in the body, as well as supporting immune function. When following an anti-Candida diet, it’s important to include high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and plant-based options like legumes, tofu, and tempeh. These protein sources provide essential amino acids without adding to Candida overgrowth.
Healthy Fats and Oils
Healthy fats and oils are essential for overall health and can help reduce inflammation in the body. Include sources such as avocado, olive oil, coconut oil, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and nuts in your anti-Candida diet. These fats provide satiety, support brain function, and contribute to a healthy hormonal balance.
Herbs and Spices
Many herbs and spices not only add flavor to your meals but also possess anti-fungal properties that can contribute to combating Candida overgrowth. Incorporate herbs and spices like garlic, ginger, oregano, cinnamon, and turmeric into your cooking to reap their potential benefits.
Probiotic-Rich Foods
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help rebalance the gut microbiome and support digestive health. Including probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, and other fermented foods in your anti-Candida diet can help restore the beneficial bacteria population in your gut.
Foods to Avoid on an Anti-Candida Diet
To effectively combat Candida overgrowth, it’s crucial to eliminate or minimize foods and beverages that can fuel its growth. Here are some categories of foods to avoid on an anti-Candida diet:
Sugar and Sweeteners
Avoiding all forms of sugar is essential when following an anti-Candida diet. This includes not only refined sugar but also natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, and agave nectar. These sweeteners can feed the Candida and hinder your progress towards balancing your gut flora.
Refined Grains and Flours
Refined grains and flours are stripped of their nutrients and fiber, leaving behind simple carbohydrates that can quickly raise blood sugar levels and contribute to Candida overgrowth. Stay away from white bread, white rice, pasta, and other refined grains and flours, and opt for whole grain alternatives to provide more fiber and a slower release of energy.
Processed Foods
Processed foods often contain a variety of additives, preservatives, and hidden sugars that can disrupt the balance of your gut flora and contribute to Candida overgrowth. Avoid packaged snacks, fast food, sugary cereals, and other processed foods that can undermine your progress in managing Candida.
Alcohol and Caffeine
Alcohol and caffeine can both have negative effects on gut health and disrupt the balance of beneficial bacteria. Alcohol can also be a source of added sugars, which should be avoided on an anti-Candida diet. It’s best to avoid or limit your intake of alcoholic beverages and caffeinated drinks like coffee and certain teas.
Dairy Products
Dairy products, especially those high in lactose, can be problematic for individuals with Candida overgrowth. Lactose is a type of sugar that can feed the Candida and inhibit progress in rebalancing the gut flora. Opt for non-dairy alternatives like almond milk, coconut milk, or hemp milk as substitutes.
High-Carb Fruits
While fruits can be a part of a healthy diet, certain high-carb fruits like bananas, grapes, and melons can contribute to Candida overgrowth due to their higher sugar content. It’s best to limit these fruits and focus on consuming lower-sugar options like berries instead.
Moldy Foods
Foods that are moldy or have a high risk of mold contamination should be avoided when dealing with Candida overgrowth. Examples include moldy cheeses, bread, and other food items with visible mold growth. Mold can exacerbate symptoms and hinder progress, so it’s important to be cautious and mindful of food quality.
Meal Planning and Preparation
Planning and preparing meals in line with an anti-Candida diet can help you make healthier and more supportive choices. Here are some tips to consider when meal planning and preparing:
Creating a Balanced Meal
A balanced anti-Candida meal should include a combination of protein, non-starchy vegetables, healthy fats, and a limited amount of complex carbohydrates. Aim to include a variety of colors and textures to ensure a diverse nutrient intake. For example, a meal could consist of grilled chicken, steamed broccoli, a side salad with avocado, and a small serving of quinoa.
Sample Meal Plans
Here are a few sample meal plans to give you an idea of how to structure your meals on an anti-Candida diet:
- Breakfast: Veggie omelet (spinach, mushrooms, bell peppers) cooked in coconut oil, a side of sauerkraut, and herbal tea.
- Lunch: Grilled salmon with roasted asparagus and cauliflower rice, dressed with olive oil and lemon juice.
- Snack: Celery sticks with almond butter and a handful of nuts.
- Dinner: Baked chicken breast with steamed Brussels sprouts and a side of quinoa pilaf.
- Dessert: Mixed berries with unsweetened coconut yogurt.
Feel free to customize your meals based on your taste preferences and dietary needs.
Cooking and Flavoring Options
Cooking meals on an anti-Candida diet can still be enjoyable and flavorful. Opt for cooking methods like grilling, baking, steaming, or sautéing in coconut oil, olive oil, or ghee. Use herbs and spices to enhance the taste of your dishes, and experiment with different flavor combinations to keep your meals interesting.
Supplements for Candida Overgrowth
In addition to following a balanced diet, certain supplements can support your efforts in addressing Candida overgrowth. Here are some supplements to consider:
Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore the balance of gut flora and support digestive health. Look for a quality probiotic supplement with various strains of bacteria to help repopulate your gut with beneficial microbes.
Antifungal Herbs and Supplements
Certain herbs and supplements contain compounds that possess antifungal properties, which can help combat Candida overgrowth. Examples include oregano oil, garlic extract, caprylic acid, grapefruit seed extract, and black walnut hull extract. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any herbal or supplement regimen.
Digestive Enzymes
Digestive enzymes can support the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, helping to alleviate digestive issues commonly associated with Candida overgrowth. Look for a broad-spectrum enzyme blend that includes proteases, amylases, and lipases to support optimal digestion.
Liver Support
The liver plays a vital role in detoxification and elimination, which is important in managing Candida overgrowth. Certain supplements like milk thistle and dandelion root can help support liver function and aid in the elimination of toxins.
Lifestyle Considerations
In addition to dietary changes and supplementation, certain lifestyle factors can impact Candida overgrowth. Consider the following lifestyle considerations:
Stress Reduction
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and disrupt the balance of gut flora, making it important to incorporate stress reduction techniques into your daily routine. Explore activities like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies to help alleviate stress.
Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity can support overall health, boost the immune system, and promote gut motility. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, cycling, dancing, or yoga, to make exercise a sustainable and enjoyable habit.
Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is crucial for healing and maintaining a healthy immune system. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. Create a relaxing bedtime routine and prioritize sleep hygiene by ensuring a cool, dark, and quiet sleep environment.
Hydration
Proper hydration is essential for overall health and can support the elimination of toxins from the body. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day and stay hydrated throughout the day. Herbal teas and infused water can also contribute to your daily fluid intake.
Managing Candida Die-Off Symptoms
When addressing Candida overgrowth, it’s common to experience a phenomenon known as Candida Die-Off or Herxheimer reaction. During this process, toxins released by dying Candida cells can cause temporary symptoms. Here are some tips for managing die-off symptoms:
What is Candida Die-Off?
Candida Die-Off occurs when a large number of Candida cells die and release toxins into the body. These toxins can overwhelm the detoxification pathways and lead to temporary symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, muscle or joint pain, brain fog, and skin rashes.
Common Symptoms
Common die-off symptoms include flu-like sensations, digestive discomfort, increased fatigue, irritability, and worsened yeast infection symptoms. It’s important to note that die-off symptoms are temporary and should subside as the body eliminates the toxins.
Strategies to Manage Die-Off
To manage die-off symptoms, it’s crucial to support the body’s detoxification systems and provide relief. Strategies to consider include drinking plenty of water to flush out toxins, incorporating detoxifying foods like leafy greens and cilantro into meals, getting adequate rest, taking warm baths with Epsom salts to aid relaxation, and considering supplements like activated charcoal or bentonite clay to help bind and eliminate toxins.
Seeking Professional Guidance
While making dietary and lifestyle changes can be beneficial, it’s essential to seek professional guidance when dealing with Candida overgrowth. Consider the following steps:
Consulting a Healthcare Practitioner
To ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan, consult with a healthcare practitioner experienced in treating Candida overgrowth. They can help assess your individual situation, provide guidance on dietary modifications and supplement recommendations, and monitor your progress throughout the healing process.
Testing for Candida Overgrowth
If you suspect Candida overgrowth, your healthcare practitioner may recommend testing to confirm the diagnosis. Stool tests, blood tests, or comprehensive digestive analysis can provide valuable information about the level of Candida overgrowth and guide the treatment plan.
Monitoring Progress
Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare practitioner are crucial to monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. They can assess your symptoms, review any test results, and provide ongoing support and guidance as you work towards rebalancing your gut flora.
Long-Term Maintenance and Prevention
Once you have successfully addressed Candida overgrowth, it’s important to maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent its recurrence. Consider the following strategies:
Reintroducing Foods
After achieving balance in your gut flora, you can gradually reintroduce certain foods that were restricted during the initial phase of the anti-Candida diet. Start with small portions and monitor your body’s response. Pay attention to how you feel and be mindful of any potential triggers.
Monitoring Sugar Consumption
Keeping your sugar intake in check is crucial for long-term maintenance. Even after addressing Candida overgrowth, it’s important to be mindful of your sugar consumption to prevent its recurrence. Opt for whole food sources of sweetness like fruit or small amounts of natural sweeteners in moderation.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Continue to prioritize a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and adequate sleep. These lifestyle factors can support the overall health of your gut and immune system, helping to keep Candida overgrowth at bay.
By understanding Candida overgrowth and implementing the principles of an anti-Candida diet, you can effectively address this imbalance and support your overall health and well-being. With the guidance of a healthcare practitioner and the commitment to making positive changes, you can regain balance and prevent the recurrence of Candida overgrowth in the long term.
Share:
Related Posts

Thai Red Curry Chicken with Rice
This Thai red curry chicken with rice recipe is rich, creamy, and full of bold flavors. A quick and satisfying one-pan meal that’s perfect for weeknight dinners.

Building Confidence Through Strength Training: A Powerful Journey for Women
Discover how building confidence through strength training empowers women physically and mentally. Learn how lifting weights can help you feel stronger, healthier, and more self-assured.

Vegetable Dumplings
Make your own delicious vegetable dumplings at home with this easy recipe. Packed with fresh veggies and flavor, these dumplings are perfect for a healthy appetizer or meatless meal.

Ashwagandha & Maca Root: Do They Help With Hormone Balance?
Curious about ashwagandha and maca root for hormone balance? Discover how these adaptogenic herbs may support women’s hormonal health, stress relief, and energy naturally.